Arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy (AAION)
All content on Eyewiki is protected by copyright law and the Terms of Service. This content may not be reproduced, copied, or put into any artificial intelligence program, including large language and generative AI models, without permission from the Academy.
Arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy (AAION)
Introduction
Arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (AAION) is an acute, often painful[1] optic neuropathy that occurs predominantly in elderly patients over age 50, but with increasing incidence each decade thereafter,[1] and can cause permanent loss of vision. Ischemia occurs at the head of the optic nerve in relation with structural crowding of the nerve fibers, impairing perfusion and leading to optic disc edema.[2] There is thought to be a genetic component to the disease, as evidence shows white persons are affected at a higher rate,[1] but it has been reported in many different races and ethnicities.
Epidemiology and Pathogenesis
As opposed to the more common nonarteritic variety (NAION), AAION accounts for 5%-10% [1] of anterior ischemic optic neuropathies (AION) and is caused by inflammation and subsequent thrombosis of the short posterior ciliary arteries (SPCAs), which originate from the ophthalmic artery. This sequence results in optic nerve head infarction.[1] The medial SPCA has been reported to be more commonly obstructed.[1] Postmortem studies of acute AAION cases show optic disc edema with necrosis of the prelaminar, laminar, and retrolaminar portions of the nerve and chronic inflammatory cell infiltrate. The prelaminar region is located between the lamina cribrosa and the surface nerve fiber layer, supplied by centripetal branches of the peripapillary choroid.[1]
Fluorescein angiographic data support the histopathological evidence of involvement of the SPCAs in AAION. Extremely poor or absent filling of the choroid has been depicted as a characteristic of AAION. Optical coherence tomography angiography may also provide clinical evidence in ischemic conditions of the optic nerve head.[3]
Studies have also suggested that dendritic cells residing in the vessel walls are key contributors to the disease. These molecular studies indicate that the dendritic cells may initiate a pathogenic cascade in addition to recruiting macrophages and T-cells. A significant immune response initiated is the “interleukin-6–type 17 helper T-cell (Th17)–interleukin-17 or interleukin-21 axis,” which can be suppressed with glucocorticoids[1] or the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved interleukin-6 inhibitor, tocilizumab (Actemra).[4]
During the COVID-19 pandemic, several studies have shown overlapping symptoms between COVID-19 and giant cell arteritis (GCA) as well as incidence of GCA after COVID-19 infection or immunization. Additional studies should be performed to further quantify this potential association. [5][6][7][8][9]
Ocular Manifestations
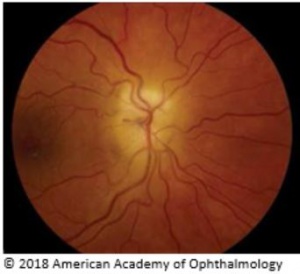
Manifestations include rapid onset of unilateral visual loss, accompanied by decreased visual acuity (typically severe: <20/200 in over 60% of the patients), visual field (altitudinal field defect is most common) or both. A relative afferent pupillary abnormality is common in unilateral or asymmetric optic neuropathies.[10] A chalky-white pallor of the optic disc with edema, which may be severe, is the hallmark of AAION, but it is not uncommon to see hyperemic swelling, as well,[1] that may be indistinguishable ophthalmoscopically from NAION. The disc most often is swollen diffusely, but a segment of more prominent involvement may be present with flame hemorrhages located adjacent to the disc, and the peripapillary retinal arterioles frequently are narrowed. Cilioretinal artery occlusion can be more specific for AAION because the artery derives its blood supply from the SPCA.[1] In addition, amaurosis fugax is an early sign that AAION may be present and that vision loss may be imminent.[1] Transient visual loss, however, is distinctly unusual in NAION.
The ocular manifestations may be due to vasculitis-related ischemia in the optic nerve, retina, choroid, orbit, or brain.
Systemic symptoms of GCA that are typically present include headache (most common) and tenderness of the temporal arteries or scalp, jaw claudication (the symptom most specific for the disorder), malaise, loss of appetite, anorexia and weight loss, fever, joint and muscle pain, and ear pain. Choroidal ischemia may be associated with the optic neuropathy and produces peripapillary pallor and edema deep to the retina. The disc of the fellow eye is of normal diameter in AAION, as is the physiologic cup.[10]
Occult GCA without overt systemic symptoms may occur in up to 20% of patients with AAlON. Other presentations, however, that are not reasonably common include hearing loss, vertigo, facial pain, lingual paralysis, and carotid bruits.[11]
Signs
On examination, patients can often show many different signs that lead to the right diagnosis. Some important signs seen with the ophthalmoscope include an optic nerve that is swollen and pale (the optic disc has a chalky color), retinal cotton-wool spots located at the posterior pole, and sometimes central retinal artery occlusion, which occurs because this artery and the SPCA are both derived from the ophthalmic artery.[1] Physical examination may also reveal diplopia, ptosis, nystagmus, or pain or nodularity upon palpitation of the temporal artery.
Diagnosis
Laboratory Studies
An elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) (up to 70 mm-120 mm/min) and/or serum C-reactive protein (CRP) may aid in diagnosis. A 97% specificity for temporal arteritis has been reported in cases of AAION in which both ESR and CRP were elevated. Patients with NA-AION do not show these types of abnormalities.[1] Other tests in GCA include platelet count for possible thrombocytosis, leukocyte count, and hemoglobin levels. Platelet count is often elevated acutely in cases of AAION and can be used in conjunction with elevated ESR and CRP levels to make a preliminary diagnosis.
Biopsy
Confirmation of the diagnosis of temporal arteritis by superficial temporal artery biopsy is recommended in cases of AION with clinical suspicion of arteritis. Positive biopsy findings (intimal thickening, internal limiting lamina fragmentation, and chronic inflammatory infiltrate with giant cells) are confirmatory for GCA. A negative biopsy does not rule out arteritis (both discontinuous arterial involvement [‘skip lesions’] and solely contralateral temporal artery inflammation may result in false-negative results) with recent reports showing a 3%-5% false-negative error rate. If the initial biopsy is found to be negative and suspicion for GCA is high, a biopsy of the contralateral temporal artery should be considered.
Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging has recently provided evidence that it may be able to distinguish between A-AION and NA-AION. The imaging scores identified the acute stage of giant cell arteritis-related anterior ischemic neuropathy with a statistically significant relationship between the side of the AION and the side of the “central bright spot,” that is, optic nerve head enhancement.[12]
Ultrasonography of the temporal artery can provide some insight as well. It reveals characteristic dark wall swelling (halo) and acute occlusions in active AAION.[13] The temporal artery duplex ultrasonogram has demonstrated a sensitivity and specificity of 87% and 96% respectively with regard to clinical diagnosis.[13] Ultrasonography provides a noninvasive technique that can be used after seeing a patient with elevated ESR, CRP, and platelet levels. It remains to be proven if ultrasonography will one day be able to obviate the temporal artery biopsy, which remains the current gold standard.
Optical coherence tomography/fluorescein angiography
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is useful in assessing sectoral disc edema and retinal nerve fiber layer thickness, as well as documenting the resolution to a normal or an atrophic optic disc. Fluorescein angiography (FA) can be used to confirm the diagnosis of AAION as well. Delayed choroidal filling may be present and can serve as a diagnostic tool for AAION, given that the test is performed soon after the onset of vision loss.[1]
Differential Diagnosis
The main differential diagnoses of AAION can include non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy, idiopathic optic neuritis, optic nerve inflammation related to syphilis or sarcoidosis, infiltrative optic neuropathies, anterior orbital lesions with optic nerve compression, and diabetic papillopathy.
Treatment
Steroids
Early steroid treatment is essential. High-dose systemic corticosteroids are standard.[1] Intravenous methylprednisolone at 1 g/day for the first 3 days has been recommended for severe cases but has not been subjected to a head-to-head trial against oral steroids in GCA. Oral prednisone in the range of 60 mg to 100 mg/day may be used initially and for follow-up to intravenous pulse therapy. Treatment is usually continued at a high dose for several months before beginning to taper, but it may be required for several years in severe cases to avoid permanent vision loss.[1]
Steroid-sparing agents
Tocilizumab is a monoclonal antibody humanized for the treatment of AAION. It works by binding to the alpha chain on the human interleukin 6 (IL-6) receptor. Through binding, tocilizumab blocks signaling and downregulates the acute phase reactions.[4] This monoclonal antibody has demonstrated effectiveness as a non-corticosteroid therapy for those dealing with AAION.[14] In some of the most recent literature, tocilizumab was very effective against corticosteroid-resistant AAION, causing symptoms to halt immediately upon first dose. However, more research into its ability to serve a protective role against bilateral blindness must be conducted to rule out any confounding variables.[14] Tocilizumab received FDA approval in 2017 for the treatment of giant cell arteritis.
Upadacitinib received FDA approval in 2025 for the treatment of giant cell arteritis. It is an oral Janus kinase-1 (JAK1) selective inhibitor which help to reduce and modulate the production of proinflammatory cytokines (17).
Other treatment options
Methotrexate is 1 of the most widely studied “steroid-sparing” agents. Also known as a chemotherapy agent, methotrexate has demonstrated some great benefits to those patients dealing with AAION. A recent study indicated that the drug could significantly increase the probability of achieving a sustained discontinuation of corticosteroid use, as well as decreasing the risks of relapses with the disease.[15] Corticosteroid therapy, while effective, can be very toxic, leading to major side effects, such as diabetes or cataracts, in almost 60% of individuals.[15] At this time, use of methotrexate may be the best way to reduce exposure to corticosteroids and their adverse effects. The best therapeutic option may be conjunction therapy, in order to decrease exposure and possible relapse for those patients with AAION.
Course and Outcome
Without treatment, visual loss occurs in 54% to 95% of GCA patients,[16] typically within 4 months.[1] With corticosteroid therapy, the rate of such decline is reduced to an estimated 13%.[16] Visual recovery of the affected eye that undergoes treatment is poor, with a 15% to 34% improvement rate, which is higher with intravenous therapy. Worsening visual acuity has been reported in 9% to 17%, despite therapy. Vision loss in both eyes is possible; however, most cases have indicated that it happens more frequently when the patient is unaware of vision loss in the first eye. The incidence of bilateral involvement depends on timing as well as how aggressively corticosteroid therapy is utilized.[1] However, if left untreated, bilateral vision loss can proceed quickly from either optic nerve, and retinal or choroidal ischemia occurs in up to 50% of cases.[4]
Additional Resources
- Boyd K, DeAngelis KD. Ischemic Optic Neuropathy. American Academy of Ophthalmology. EyeSmart/Eye health. https://www.aao.org/eye-health/diseases/ischemic-optic-neuropathy-3. Accessed March 14, 2019.
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.16 1.17 Hayreh SS. Ischemic optic neuropathy. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2009 Jan;28(1):34-62. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2008.11.002. Epub 2008 Nov 27. PMID: 19063989.
- ↑ Arnold AC. Ischemic optic neuropathies. Ophthalmol Clin North Am. 2001 Mar;14(1):83-98. PMID: 11370574.
- ↑ Balducci N, Morara M, Veronese C, Barboni P, Casadei NL, Savini G, Parisi V, Sadun AA, Ciardella A. Optical coherence tomography angiography in acute arteritic and non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2017 Nov;255(11):2255-2261. doi: 10.1007/s00417-017-3774-y. Epub 2017 Aug 31. PMID: 28861697.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Vionnet J, Buss G, Mayer C, Sokolov AA, Borruat FX, Spertini F. Tocilizumab for giant cell arteritis with corticosteroid-resistant progressive anterior ischemic optic neuropathy. Joint Bone Spine. 2017 Oct;84(5):615-619. doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2017.04.009. Epub 2017 May 9. PMID: 28499892.
- ↑ Mehta P, Sattui SE, van der Geest KSM, Brouwer E, Conway R, Putman MS, Robinson PC, Mackie SL. Giant Cell Arteritis and COVID-19: Similarities and Discriminators. A Systematic Literature Review. J Rheumatol. 2021 Jul;48(7):1053-1059. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.200766. Epub 2020 Oct 15. PMID: 33060304.
- ↑ Greb CS, Aouhab Z, Sisbarro D, Panah E. A Case of Giant Cell Arteritis Presenting After COVID-19 Vaccination: Is It Just a Coincidence? Cureus. 2022 Jan 25;14(1):e21608. doi: 10.7759/cureus.21608. PMID: 35228965; PMCID: PMC8873313.
- ↑ Jonathan GL, Scott FM, Matthew KD. A Case of Post-COVID-19-Associated Paracentral Acute Middle Maculopathy and Giant Cell Arteritis-Like Vasculitis. J Neuroophthalmol. 2021 Sep 1;41(3):351-355. doi: 10.1097/WNO.0000000000001348. PMID: 34415268.
- ↑ Au BWY, Ku DJ, Sheth SJ. Thinking Beyond Giant Cell Arteritis in COVID-19 Times. J Neuroophthalmol. 2022 Mar 1;42(1):e137-e139. doi: 10.1097/WNO.0000000000001271. PMID: 33734151.
- ↑ Mejren A, Sørensen CM, Gormsen LC, Tougaard RS, Nielsen BD. Large-vessel giant cell arteritis after COVID-19 vaccine. Scand J Rheumatol. 2022 Mar;51(2):154-155. doi: 10.1080/03009742.2021.1961401. Epub 2021 Sep 28. PMID: 34582316.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Beck RW, Servais GE, Hayreh SS. Anterior ischemic optic neuropathy. IX. Cup-to-disc ratio and its role in pathogenesis. Ophthalmology. 1987 Nov;94(11):1503-8. PMID: 3684223.
- ↑ Minagar A, Fowler M, Harris MK, Jaffe SL. Neurologic presentations of systemic vasculitides. Neurol Clin. 2010 Feb;28(1):171-84. doi: 10.1016/j.ncl.2009.09.015. PMID: 19932380.
- ↑ Remond P, Attyé A, Lecler A, Lamalle L, Boudiaf N, Aptel F, Krainik A, Chiquet C. The Central Bright Spot Sign: A Potential New MR Imaging Sign for the Early Diagnosis of Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy due to Giant Cell Arteritis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2017 Jul;38(7):1411-1415. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A5205. Epub 2017 May 11. PMID: 28495949; PMCID: PMC7959905.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Schmidt WA. Role of ultrasound in the understanding and management of vasculitis. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2014 Apr;6(2):39-47. doi: 10.1177/1759720X13512256. PMID: 24688604; PMCID: PMC3956137.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Villiger PM, Adler S, Kuchen S, Wermelinger F, Dan D, Fiege V, Bütikofer L, Seitz M, Reichenbach S. Tocilizumab for induction and maintenance of remission in giant cell arteritis: a phase 2, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2016 May 7;387(10031):1921-7. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00560-2. Epub 2016 Mar 4. PMID: 26952547.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 Mahr AD, Jover JA, Spiera RF, Hernández-García C, Fernández-Gutiérrez B, Lavalley MP, Merkel PA. Adjunctive methotrexate for treatment of giant cell arteritis: an individual patient data meta-analysis. Arthritis Rheum. 2007 Aug;56(8):2789-97. doi: 10.1002/art.22754. PMID: 17665429.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 Arnold AC. Ischemic optic neuropathy. Clinical neuro-ophthalmology 1 2005: 349-384.
17. Blockmans D, Penn SK, Setty AR, Schmidt WA, Rubbert-Roth A, Hauge EM, Keen HI, Ishii T, Khalidi N, Dejaco C, Cid MC, Hellmich B, Liu M, Zhao W, Lagunes I, Romero AB, Wung PK, Merkel PA; SELECT-GCA Study Group. A Phase 3 Trial of Upadacitinib for Giant-Cell Arteritis. N Engl J Med. 2025 May 29;392(20):2013-2024. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2413449. Epub 2025 Apr 2. PMID: 40174237.